

In his 1949 book The Concept of Mind, Gilbert Ryle, an English philosopher, introduced the term “category mistake.” He gave the example of a visitor to the University of Oxford who sees colleges and a splendid library and then asks, “But where is the university?” The category mistake is obvious: A university is an institution, not a collection of buildings.
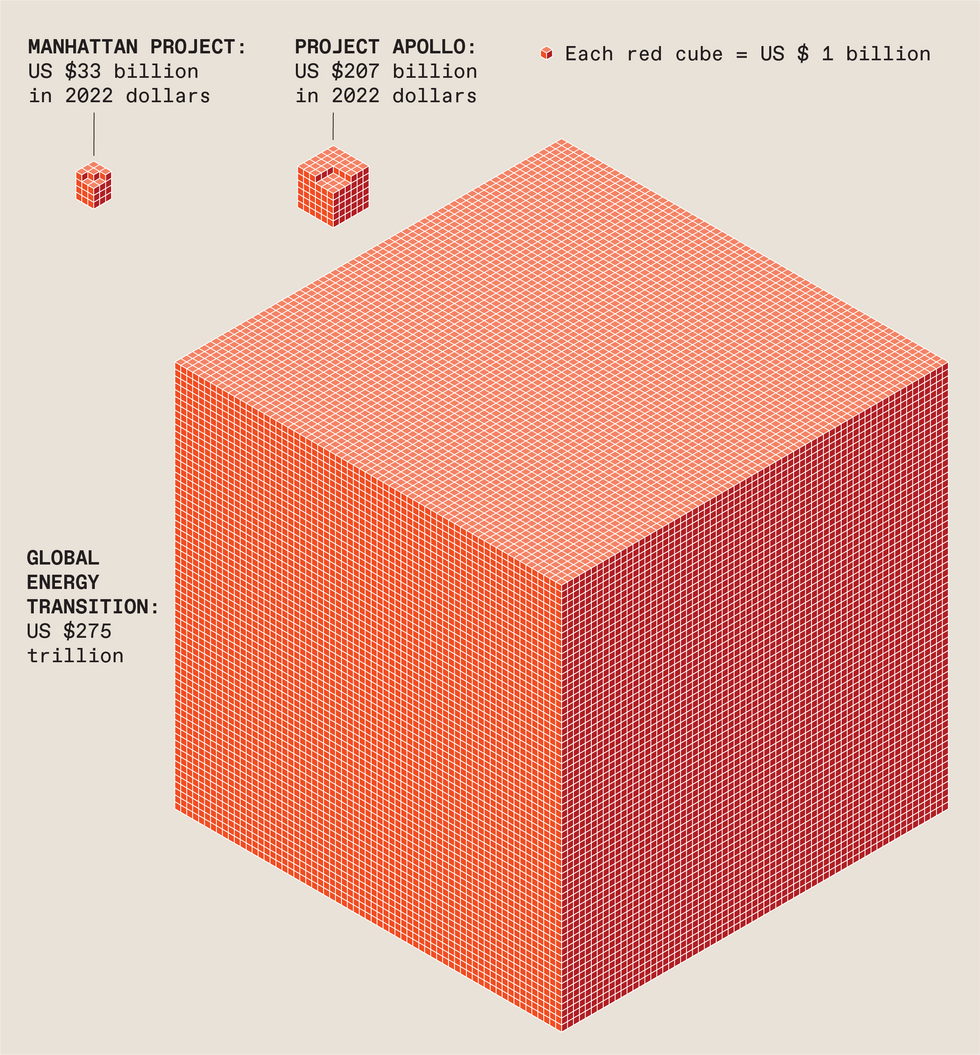
Today, no category mistake is perhaps more consequential than the all-too-common view of the global energy transition. The error is to think of the transition as the discrete, well-bounded task of replacing carbon fuels by noncarbon alternatives. The apparent urgency of the transition leads to calls for confronting the challenge just as the United States dealt with two earlier ones: winning the nuclear-arms race against Nazi Germany and the space race against the Soviet Union. The Manhattan Project produced an atomic bomb in three years, and Project Apollo put two U.S. citizens on the moon in July 1969, eight years after President Kennedy had announced the goal.
But difficult and costly as those two endeavors were, they affected only small parts of the economy, their costs were relatively modest, and the lives of average citizens were hardly affected. It is just the opposite for the decarbonization of the energy supply.
Ours is an overwhelmingly fossil-fueled civilization, and the size and complexity of our extensive supersystem of fuel extraction, processing, distribution, storage, and conversion means that a complete displacement of it will directly affect every person and every industry, not least the growing of food and the long-distance transport of goods and people. The costs will be stupendous.
Affluent nations would have to devote on the order of 15 to 20 percent of their annual economic product to the task of decarbonizing the economy.
By the time the Manhattan Project ended in 1946, it had cost the country nearly US $2 billion, about $33 billion in today’s money, the total equal to only about 0.3 percent of the 1943-45 gross domestic product. When Project Apollo ended in 1972, it had cost about $26 billion, or $207 billion in today’s money; over 12 years it worked out annually to about 0.2 percent of the country’s 1961-72 GDP.
Of course, nobody can provide a reliable account of the eventual cost of global energy transition because we do not know the ultimate composition of the new primary energy supply. Nor do we know what shares will come from converting natural renewable flows, whether we will use them to produce hydrogen or synthetic fuels, and the extent to which we will rely on nuclear fission (and, as some hope, on fusion) or from other, still unknown options.
 Chris Philpot; Sources: CTBTO Preparatory Commission; ScienceDirect; McKinsey Global Institute
Chris Philpot; Sources: CTBTO Preparatory Commission; ScienceDirect; McKinsey Global Institute
But a recent attempt to estimate such costs confirms the magnitude of the category mistake. The McKinsey Global Institute, in a highly conservative estimate, puts the cost at $275 trillion between 2021 and 2050. That is roughly $9.2 trillion a year, compared with the 2021 global economic product of $94 trillion. Such numbers imply an annual expenditure of about 10 percent of today’s world economic product. And because the world’s low-income countries could not carry such burdens, affluent nations would have to devote on the order of 15 to 20 percent of their annual economic product to the task. Such shares are comparable only to the spending that was required to win World War II.
This article appears in the October 2022 print issue as “Decarbonization Is Our Greatest Challenge.”
Reference: https://ift.tt/DyJPYGR
No comments:
Post a Comment